The battery industry is experiencing a surge in innovation, driven by the pursuit of more efficient and higher-performing technologies that can offer significant market advantages. Recently, there has been a resurgence of interest in sodium iron phosphate battery (NaFePO4 battery) due to their economic benefits. Sodium-ion battery is gaining traction in energy storage and electric mobility, but several limitations still need to be addressed before they can be widely commercialized. Let's explore the characteristics and potential of sodium battery.
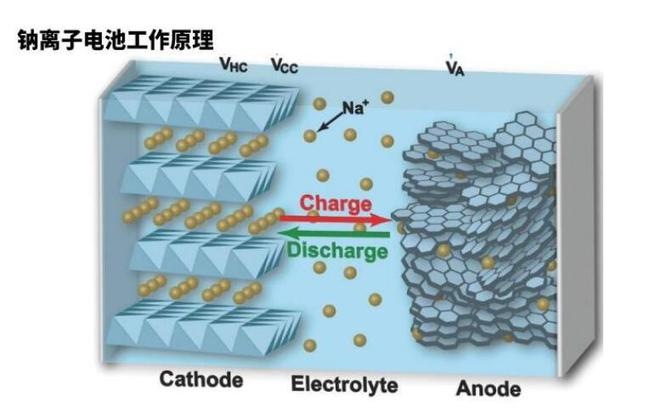
NaFePO4 battery operate on principles similar to lithium-ion battery. Both sodium and lithium are alkali metals located in Group 1 of the periodic table, sharing many physical and chemical properties. Research on sodium battery began between 1970 and 1990, around the same time as lithium battery. However, lithium battery were commercialized more successfully, sidelining sodium battery.
NaFePO4 battery and lithium-ion battery share the same basic working principle. Both use ions to store and transfer energy. During charging, sodium ions move from the cathode (positive electrode) to the anode (negative electrode) through the electrolyte. During discharge, the ions return to the cathode, generating an electric current.
A sodium battery consists of a cathode made of sodium-containing material, a carbon-based anode, and a liquid electrolyte with sodium ions. This setup allows ions to move between the cathode and anode, enabling energy storage and release.
Chemically, sodium differs significantly from lithium. Sodium ions are larger and heavier, leading to greater mechanical stress during charge cycles, which causes faster cell degradation. Consequently, sodium battery have a shorter cycle life compared to lithium battery. Additionally, sodium battery have a lower standard reduction potential, resulting in a lower maximum voltage and energy density. A sodium battery stores about 40% less energy than a lithium battery of the same weight.
1. Abundance and Low Cost: Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, making it economically competitive.
2. Safety: Sodium-based cells are non-flammable and less prone to explosions or short circuits.
3. Temperature Resilience: They operate effectively in a wider temperature range (-20°C to 60°C) compared to lithium battery (0°C to 50°C).
4. Environmental Impact: The extraction and processing of sodium require less energy, reducing environmental impact.
1. Low Energy Density: Sodium battery have lower energy density (140-160 Wh/kg) compared to lithium-ion battery (180-250 Wh/kg).
2. Short Cycle Life: The larger mass of sodium ions causes greater mechanical stress, leading to faster degradation of the anode material, typically graphite.
Sodium battery could serve as an alternative to lithium battery in applications where cost is more critical than performance. They are particularly suited for stationary energy storage systems, such as those used in photovoltaic and wind power systems, due to their safety and ability to handle frequent charge-discharge cycles. However, their current short cycle life limits their widespread use in these applications.
The NaFePO4 battery market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 27% over the next decade, with production expected to increase from 10 GWh in 2025 to approximately 70 GWh by 2033. The similarity in production technology between sodium and lithium cells could facilitate the transition and make sodium-ion battery more cost-effective.
Major players in the battery manufacturing industry, like CATL, are exploring sodium-ion technology. CATL has proposed a hybrid battery pack combining sodium-ion and lithium-ion battery to leverage the strengths of both technologies. This innovation aims to overcome sodium battery' drawbacks and reduce the overall cost of lithium battery.
While sodium-ion technology faces challenges, ongoing research and significant investments are likely to overcome these barriers. NaFePO4 battery could offer tangible benefits in applications where energy density is less critical, providing a viable alternative to lithium battery.
Next:34pcs 3.2V 105Ah and 20Ah cells shipped to Ecuador
Previous:CATL successfully tested a 4-ton aircraft!
Contact Person: Miss. Elsa Liu
| WhatsApp : | +8617763274209 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763274209 |
| WeChat : | 17763274209 |
| Email : | Elsa@lifepo4-battery.com |