With the rapid development of electric vehicles, smartphones, and renewable energy, battery technology has become the cornerstone of modern technology. Among various battery technologies, lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion) have long dominated the market. However, in recent years, semi-solid-state batteries (SSB) have emerged as a new technology, gradually attracting widespread attention. So, what exactly are the differences between semi-solid-state batteries and lithium-ion batteries? What are their respective advantages and disadvantages? This article will provide a detailed analysis.
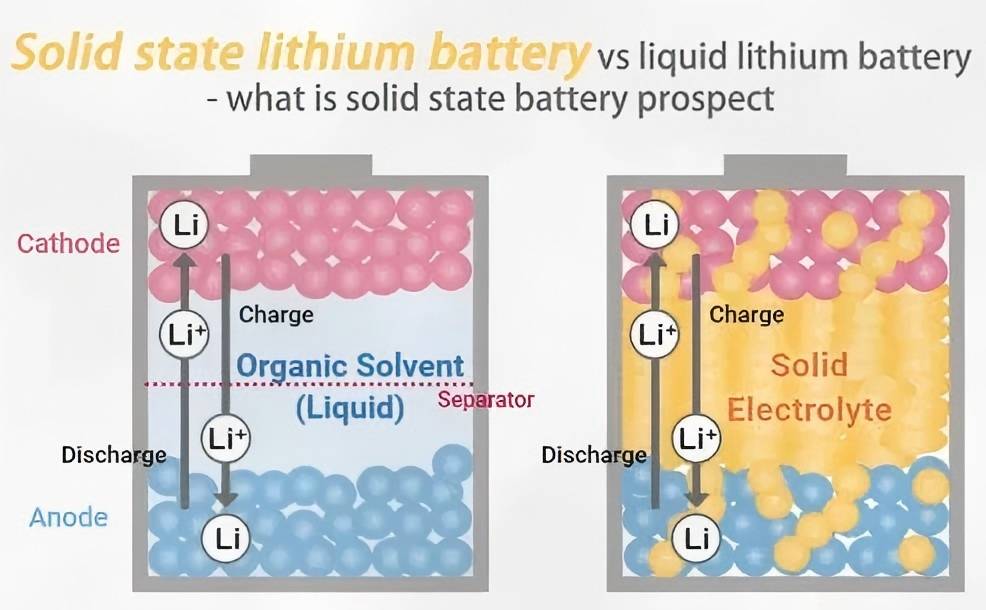
Lithium-ion batteries are one of the most widely used battery technologies, spanning fields from consumer electronics to electric vehicles. Their operating principle is based on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes. During charging, lithium ions migrate from the positive electrode (usually lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, etc.) to the negative electrode (usually graphite); during discharging, lithium ions move back to the positive electrode, releasing electrical energy.
High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, offering a longer range.
Mature Technology: After decades of development, the production processes and supply chains for lithium-ion batteries are well-established, and costs have been decreasing.
Fast Charging: They support higher charging rates, making them suitable for modern fast-charging demands.
Safety Concerns: Lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolytes, which pose risks such as leakage, overheating, or even fire.
Limited Lifespan: Battery capacity gradually declines with increased charge and discharge cycles.
Resource Dependency: The supply of key materials like lithium and cobalt can be affected by geopolitical factors and resource limitations.
Semi-solid-state batteries are a new type of battery technology that sits between traditional liquid lithium-ion batteries and full solid-state batteries. They use a semi-solid electrolyte that contains both liquid and solid components. This design retains the high ionic conductivity of liquid electrolytes while incorporating the stability and safety benefits of solid-state electrolytes.
Higher Safety: The semi-solid electrolyte reduces the risks of leakage and fire, enhancing the overall safety of the battery.
Higher Energy Density: Thanks to the use of new materials and structures, semi-solid-state batteries are expected to have a higher energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Longer Lifespan: Semi-solid-state batteries have better chemical stability, allowing for more charge and discharge cycles.
Faster Charging: The higher ionic conductivity of semi-solid-state batteries could enable faster charging rates.
Immature Technology: Semi-solid-state batteries are still in the early stages of development and commercialization, with production processes and cost control not yet fully mature.
Higher Cost: Due to the use of new materials and technologies, semi-solid-state batteries are currently more expensive to manufacture.
Incomplete Supply Chain: The supply chain for the necessary materials and equipment is not yet fully established, which could affect large-scale production.
| Feature | Lithium-ion Battery | Semi-solid-state Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Liquid electrolyte | Semi-solid electrolyte |
| Energy Density | High | Higher (potential) |
| Safety | Low (risk of leakage, fire) | Higher |
| Lifespan | Limited (500-1000 cycles) | Longer (potential) |
| Charging Speed | Fast | Faster (potential) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher (currently) |
| Technology Maturity | Very mature | Early stage |
The advent of semi-solid-state batteries brings new possibilities across various fields:
Electric Vehicles: Higher energy density and safety can significantly improve the driving range and user experience of electric vehicles.
Consumer Electronics: Faster charging speeds and longer battery life will enhance the performance of devices like smartphones and laptops.
Energy Storage Systems: The stability and long lifespan of semi-solid-state batteries make them an ideal choice for renewable energy storage.
Although semi-solid-state batteries currently face technical and cost challenges, they are expected to achieve commercialization breakthroughs in the coming years as research progresses and the industrial chain matures.
Lithium-ion batteries, as the dominant technology today, still have significant advantages in terms of performance and cost. However, their safety and resource dependency issues cannot be overlooked. As a new and emerging technology, semi-solid-state batteries, though still in their early stages and costly, show great potential in energy density, safety, and lifespan.
With advances in technology and market demand, semi-solid-state batteries are expected to complement lithium-ion batteries and jointly drive innovation in battery technology. Whether you're a technology enthusiast, an electric vehicle user, or a professional in the energy industry, understanding the differences and development trends of these two battery technologies will help you better seize future opportunities.
Next:CORNEX First Batch of 688Ah Ultra-large Capacity Battery Cells Rolls Off the Production Line!
Previous:6pcs Winston TS-LYP 160AHA-B battery Ship to Australia
Contact Person: Miss. Elsa Liu
| WhatsApp : | +8617763274209 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763274209 |
| WeChat : | 17763274209 |
| Email : | Elsa@lifepo4-battery.com |