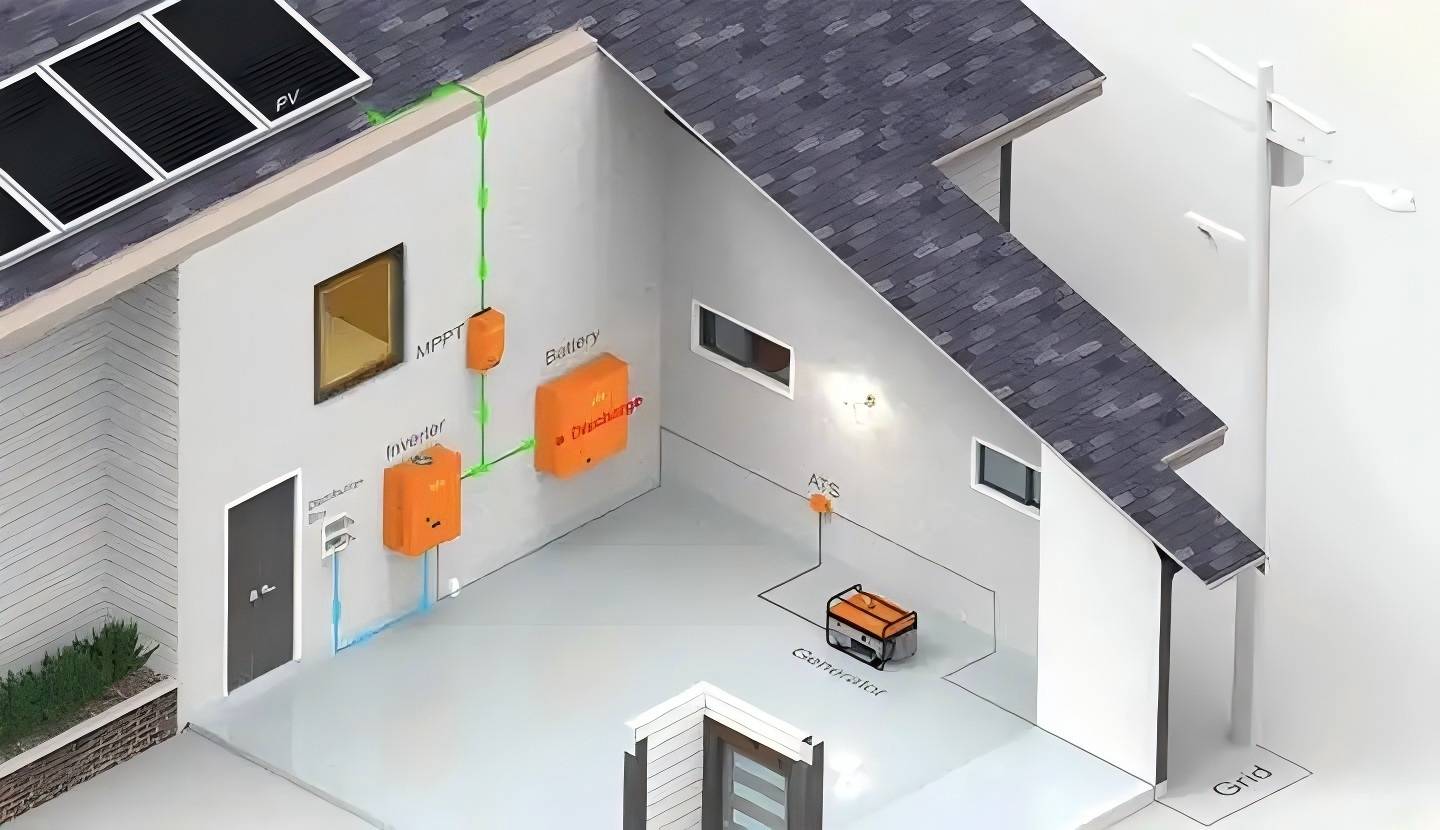
Off-grid living refers to a lifestyle where one does not rely on the public power grid but instead generates electricity through renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydro power. As people become more aware of environmental issues and increasingly pursue an independent, self-sufficient lifestyle, off-grid living is gaining popularity. However, for off-grid living to succeed, a stable and reliable battery system is crucial. The choice of battery capacity directly impacts the stability and safety of the power supply. So, how do you choose the right battery capacity for off-grid living? Below are some key factors and calculation steps to help you make the right decision.
Before choosing the appropriate battery capacity, you first need to determine your daily power consumption. This is the foundation for selecting the right battery size. To accurately estimate your daily electricity usage, you need to list all your electrical devices and their power ratings, then calculate their daily energy consumption.
Calculation Method:
Power (W) = Rated power of the device (e.g., light bulbs, refrigerators, TVs)
Usage Time (hours) = The number of hours each device is used daily
Daily Power Consumption (Wh) = Power (W) × Usage Time (hours)
For example:
A 40-watt LED light bulb used for 6 hours a day will consume:
40W × 6h = 240Wh
A 150-watt refrigerator running for 12 hours a day will consume:
150W × 12h = 1800Wh
Sum up the daily power consumption of all your devices to get the total daily power requirement. For instance, if the total daily consumption of all your devices is 3000Wh (3kWh), then you need to ensure that the battery and solar system can provide at least this much energy.
The choice of battery type has a significant impact on the quality of off-grid living. The main types of batteries are lead-acid and lithium-ion, each with its own pros and cons:
Lead-Acid Batteries
Pros: Lower cost, mature technology, suitable for users on a budget.
Cons: Require more space, lower charging efficiency, higher maintenance needs, shorter lifespan (typically 3-5 years), and they cannot be fully discharged (Depth of Discharge or DoD is around 50%).
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Pros: High efficiency, large energy density, smaller size, longer lifespan (typically over 10 years), minimal maintenance, higher DoD (80%-90%), faster charging.
Cons: Higher initial cost.
For most off-grid users, lithium-ion batteries are becoming the preferred choice due to their efficiency, durability, and smaller space requirements.
The Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to the percentage of a battery's capacity that can be used without significantly affecting its lifespan. Different battery types have different DoD values:
Lead-Acid Batteries typically have a DoD of about 50%, meaning that only 50% of the battery's capacity can be used, while the remaining 50% should be kept as a "reserve" to avoid over-discharging and to extend the battery's lifespan.
Lithium-Ion Batteries usually have a DoD of 80%-90%, allowing you to use a greater portion of the battery's total capacity without significantly impacting its lifespan.
Thus, when choosing a battery, you need to consider how long you want the battery to last. Typically, lithium-ion batteries provide a higher DoD, allowing you to make more efficient use of the stored energy.
Once you have determined your daily power consumption and chosen the battery type, you can begin calculating the required battery capacity. Let's assume you need 3000Wh of energy per day and choose a 12V lithium-ion battery. You should also take the following factors into account:
Battery Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Suppose the DoD of the lithium-ion battery you choose is 90%, meaning you can use 90% of the battery's total capacity. For safety, we typically recommend selecting a battery with slightly more capacity than your daily requirement.
Calculation Steps:
1. Calculate your daily power needs:
Assume your daily power consumption is 3000Wh.
2. Calculate the required battery capacity:
[ Battery Capacity (Wh) = Daily Power Consumption (Wh) ÷ Depth of Discharge (DoD) ]
[ Battery Capacity (Wh) = 3000Wh ÷ 0.9 ≈ 3333Wh ]
3. Convert Wh to amp-hours (Ah):
[ Battery Capacity (Ah) = Battery Capacity (Wh) ÷ Voltage (V) ]
[ Battery Capacity (Ah) = 3333Wh ÷ 12V ≈ 278Ah ]
Therefore, you would need a battery with a capacity of approximately 3000Wh (around 278Ah) at 12V to meet your daily power needs. Considering battery degradation and emergency redundancy, it is recommended to choose a battery with a larger capacity or use multiple batteries in parallel.
In off-grid living, the battery is usually paired with a solar power system. The size of the solar system should be capable of meeting your daily charging needs, while the battery provides backup power during the night or on cloudy days. When selecting a battery, you need to ensure that the battery's charging and discharging capacities are well-matched with the power generated by your solar panels.
For example, if your solar panels can provide 4000Wh of energy per day, you need to ensure that the battery can store enough energy to cover several days without sunlight. For this reason, the battery capacity should consider at least two to three days of power consumption.
Batteries are not a "set-it-and-forget-it" solution; they will gradually lose some of their storage capacity over time. Therefore, regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring stable off-grid living. Some maintenance tips include:
Regularly check the battery's voltage and capacity to ensure there is no over-discharging or overcharging.
Avoid extreme temperatures, as both high and low temperatures can negatively affect battery performance, particularly for lithium-ion batteries.
Keep the battery clean and ensure there is no dust, moisture, or corrosive materials affecting the electrical connections.
Choosing the right battery capacity is essential for successful off-grid living. By assessing your daily power consumption, selecting the right battery type, calculating the required capacity, and ensuring compatibility with your solar system, you can build a reliable off-grid power system. The battery's Depth of Discharge (DoD), durability, and ongoing maintenance should all be considered. As off-grid living becomes more popular, properly sized and well-maintained batteries not only improve the quality of life but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
Next:LFP Battery vs. Ternary Lithium Battery: Which is Best for Your EV
Previous:Everything you need to know about the Sodium Ion Battery
Contact Person: Miss. Elsa Liu
| WhatsApp : | +8617763274209 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763274209 |
| WeChat : | 17763274209 |
| Email : | Elsa@lifepo4-battery.com |