1. LiFePO4 Battery Structure
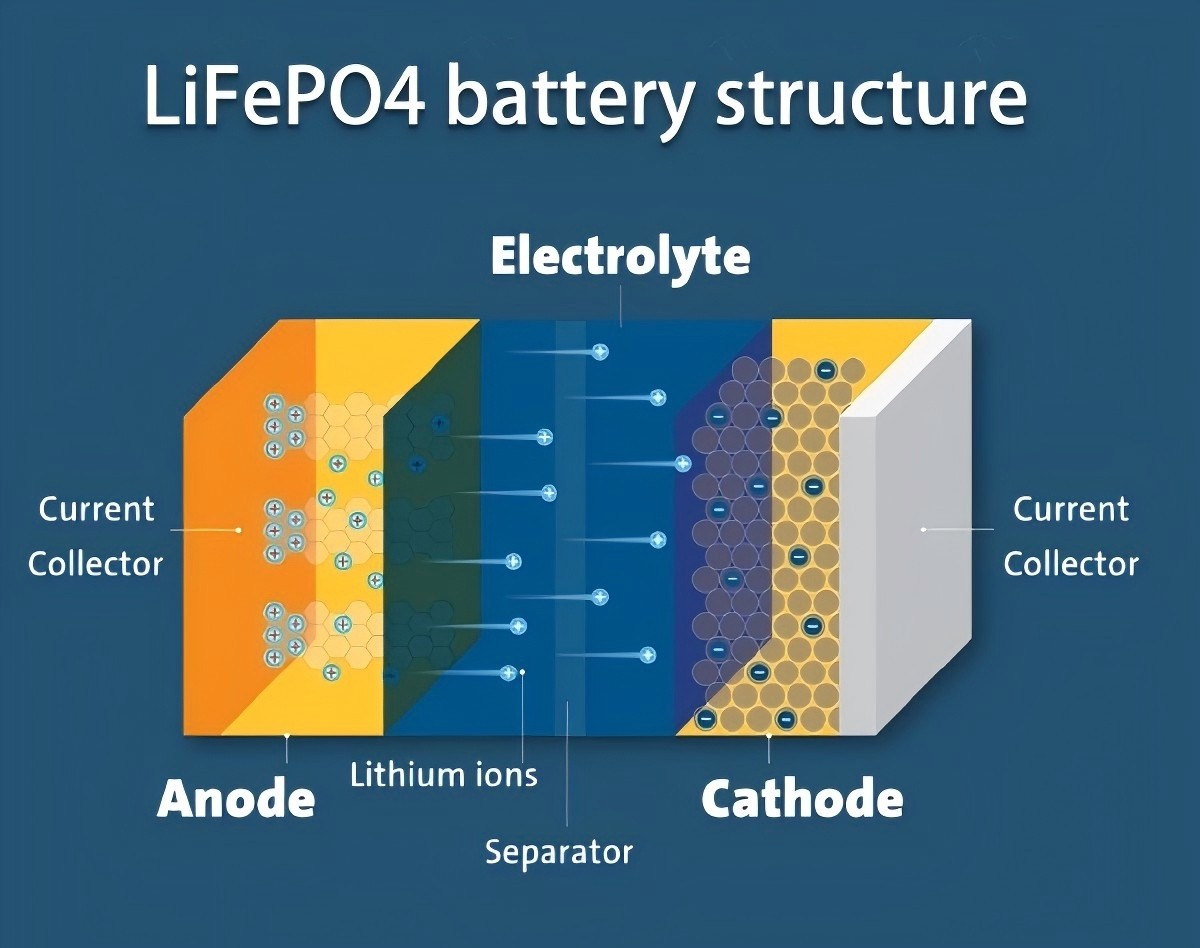
The components of LiFePO4 Battery include a positive electrode, negative electrode, electrolyte, diaphragm, positive and negative electrode leads, center terminal, safety valve, sealing ring, and shell.
· Positive Electrode: Made of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) with an olivine structure, connected to the battery’s positive terminal by aluminum foil.
· Separator: A polymer layer that separates the positive and negative electrodes, allowing lithium ions (Li+) to pass through while blocking electrons (e-).
· Negative Electrode: Composed of carbon (graphite) and connected to the battery’s negative terminal by copper foil.
The low conductivity, stability, and safety performance of the LFP cathode material define its unique characteristics.
2. LiFePO4 Battery Principle
· Charging Process: When the LFP battery is charged, lithium ions migrate from the surface of the LiFePO4 crystal to the electrolyte, pass through the separator, and embed into the graphite lattice on the negative electrode. Electrons flow through an external circuit to balance the charge.
· Discharging Process: When the LFP battery is discharged, lithium ions move from the graphite crystal back to the LiFePO4 crystal. The electrons flow in the reverse direction to balance the charge.
Recommended Charging Method
Use the CCCV (Constant Current Constant Voltage) charging method:
· Constant Current: Recommended at 0.3C.
· Constant Voltage: Recommended at 3.65V.
Are LFP battery and lithium-ion battery chargers the same?
* The charging method of both batteries is a constant current and then a constant voltage (CCCV), but the constant voltage points are different.
* The nominal voltage of a lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.2V, and the charging cut-off voltage is 3.6V.
* The nominal voltage of ordinary lithium batteries is 3.6V, and the charging cut-off voltage is 4.2V.
Can I charge LiFePO4 batteries with solar?
Solar panels cannot directly charge lithium-iron phosphate battery. Because the voltage of solar panels is unstable, they cannot directly charge lithium-iron phosphate batteries. A voltage stabilizing circuit and a corresponding lithium iron phosphate battery charging circuit are required to charge it.
Charging lithium iron phosphate batteries with a generator
The generator cannot directly charge the LiFePO4 battery because the power generated by the generator is alternating or pulsed direct current. The LiFePO4 battery must be charged with regulated direct current.
1. Determine Safe Discharge Rate:Maximum discharge rate is typically 1C to 3C.Exceeding this rate may damage the battery.
2. Connect the Load:Ensure secure connections and correct polarity.
3. Monitor Voltage:Avoid discharging below 2.5V per cell to prevent damage.
4. Manage Discharge Rate:Reduce the rate if the battery overheats.
5. Stop at Minimum Voltage:Discharge only until 2.5V per cell.
6. Store Properly:Store at 50% state of charge in a cool, dry place.
1. Avoid Overcharging/Overdischarging:Maintain charge between 40-80% for optimal longevity.
2. Control Charging Time:Use a compatible charger and avoid overcharging.
3. Keep Clean:Regularly clean the battery surface to prevent contamination.
4. Avoid Extreme Temperatures:Operate within 5°C to 35°C.
5. Protect from Physical Damage:Prevent crushing or deformation.
6. Perform Regular Maintenance:Check connections, clean terminals, and inspect for issues.
7. Use a Dedicated Charger:Ensure the charger’s specifications match the battery.
1. Standard Charging Current:Between 0.2C to 1C (e.g., 20A to 100A for a 100Ah battery).
2. Fast Charging Current:Between 1C to 3C for faster charging (e.g., 100A to 300A for a 100Ah battery).
3. Balancing Charging:0.1C to 0.2C for equalizing cells (e.g., 10A to 20A for a 100Ah battery).
4. Trickle Charging:0.01C to 0.05C to maintain charge (e.g., 1A to 5A for a 100Ah battery).
1. Constant Voltage Charging:Maintains a fixed voltage. Not widely used due to potential overcurrent issues.
2. Constant Current Charging:Maintains a fixed current but becomes less efficient in later stages.
3. Constant Current and Constant Voltage Charging:Combines the benefits of both methods.
4. Chopping Charge:Uses intermittent charging to improve ion utilization and battery capacity.
What is the best way to charge a LiFePO4 battery?
The best way to charge a LiFePO4 battery is to use a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries, which provides the appropriate voltage and charging algorithm for optimal performance and safety.
Should I charge LiFePO4 100%?
Charging LiFePO4 batteries to around 80-90% of their capacity for regular use is generally recommended. Charging them to 100% occasionally can help balance the cells, but frequent full charges may reduce their lifespan.
Do I need a special charger for the LiFePO4 battery?
Yes, using a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries is important. LiFePO4 batteries require a different charging algorithm than other battery chemistries, and using a charger with the correct voltage and charging profile ensures safe and efficient charging.
How do I know if my LiFePO4 battery is fully charged?
By monitoring the charging voltage and current, you can determine if lithium iron phosphate battery is fully charged. When the battery reaches its maximum voltage and the charging current drops to a very low level (usually below 5% of the battery’s capacity), it is an indication that the battery is fully charged.
Contact Person: Miss. Elsa Liu
| WhatsApp : | +8617763274209 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763274209 |
| WeChat : | 17763274209 |
| Email : | Elsa@lifepo4-battery.com |